最近迁移了自己的小服务器,也顺便把本机的环境重新设置了一下,其中环节还是有点复杂的小细节的。所以打算整理下思路,方便以后再设置同样环境。

对于服务器
目前常用的系统主要是 Ubuntu 和 FreeBSD,到手第一步便是更换到国内的镜像源。
对于 FreeBSD 目前可用的有中科大的源,pkg 的配置文件位置为:/etc/pkg/FreeBSD.conf。
FreeBSD: {
url: "pkg+http://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/freebsd-pkg/${ABI}/latest",
mirror_type: "srv",
signature_type: "fingerprints",
fingerprints: "/usr/share/keys/pkg",
enabled: yes
}
对于 Ubuntu,随便选一个就可以了。配置文件位于:/etc/apt/sources.list。清华大学开源软件镜像站的 Ubuntu 镜像使用帮助
# 默认注释了源码镜像以提高 apt update 速度,如有需要可自行取消注释
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-security main restricted universe multiverse
# 预发布软件源,不建议启用
# deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
# deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ focal-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
更换 Shell
Ubuntu 和 FreeBSD 默认 shell 分别是 bash 和 sh,下一步就是切换到 zsh。
# Ubuntu
apt install zsh -y
# FreeBSD
pkg install zsh
Oh my zsh 的安装非常的简单,复制一条命令即可。但困难的地方在于我的服务器可能经常连不上 Github,因为它是通过 clone Github 上的仓库来进行安装的。
sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/robbyrussell/oh-my-zsh/master/tools/install.sh)"
研究了一下,可以找个 Github 的镜像站手动安装。不过这种方法还是有一定风险的,毕竟是直接从别人的站点下载的东西。比较推荐的还是 Gitee 的 镜像。还有个 fastgit 目前也是能用的。

Oh my zsh 也写了详细了 manual-installation 参考着修改下源的地址就可以了。
# Clone the repository
git clone https://gitee.com/mirrors/ohmyzsh.git ~/.oh-my-zsh
# Create a new zsh configuration file
cp ~/.oh-my-zsh/templates/zshrc.zsh-template ~/.zshrc
# Change your default shell
chsh -s $(which zsh)
Plugins
我比较常用的是 zsh-autosuggestions 与 zsh-syntax-highlighting,比较可惜的是这俩 Gitee mirror 上都还没有。
git clone https://github.com/zsh-users/zsh-autosuggestions ${ZSH_CUSTOM:-~/.oh-my-zsh/custom}/plugins/zsh-autosuggestions
# Add to .zshrc
plugins=(git zsh-autosuggestions)
git clone https://github.com/zsh-users/zsh-syntax-highlighting.git
echo "source ${(q-)PWD}/zsh-syntax-highlighting/zsh-syntax-highlighting.zsh" >> ${ZDOTDIR:-$HOME}/.zshrc
source ./zsh-syntax-highlighting/zsh-syntax-highlighting.zsh
Theme
通常用的是 powerlevel10k 或者 random。
对于 powerlevel10k 可以:
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/romkatv/powerlevel10k.git ${ZSH_CUSTOM:-$HOME/.oh-my-zsh/custom}/themes/powerlevel10k
# or
git clone --depth=1 https://gitee.com/romkatv/powerlevel10k.git ${ZSH_CUSTOM:-$HOME/.oh-my-zsh/custom}/themes/powerlevel10k
还需要添加一下环境变量
# To customize prompt, run `p10k configure` or edit ~/.p10k.zsh.
[[ ! -f ~/.p10k.zsh ]] || source ~/.p10k.zsh
POWERLEVEL9K_DISABLE_CONFIGURATION_WIZARD=true
Sudo with out password
Run sudo without password on mostly Linux
- Backup /etc/sudoers file, run:
sudo cp /etc/sudoers /root/sudoers.bak
- Edit the /etc/sudoers file on CentOS:
sudo visudo
- Run /usr/sbin/rebootcommand without password on CentOS:
xfy ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
- Save and exit the file.
Docker mirror
对于使用 systemd 的系统(Ubuntu 16.04+、Debian 8+、CentOS 7), 在配置文件 /etc/docker/daemon.json 中加入:
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://docker.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/"]
}
重新启动 dockerd:
sudo systemctl restart docker
对于语言
目前常用的主要是 Node.js 与 Rustup,这俩官方地址的速度也是时好时坏。好在淘宝和中科大有他们的镜像源。
Node.js
主要用的是 nvm,类似于 Oh my zsh,可以 manual-install。
git clone https://gitee.com/mirrors/nvm.git .nvm
然后导出对应的变量到当前的 shell 配置文件中:
export NVM_DIR="$HOME/.nvm"
[ -s "$NVM_DIR/nvm.sh" ] && \. "$NVM_DIR/nvm.sh" # This loads nvm
[ -s "$NVM_DIR/bash_completion" ] && \. "$NVM_DIR/bash_completion" # This loads nvm bash_completion
其次就是安装 Node.js 本身了,nodejs.org 的速度大部分情况下都是很快的,偶尔也会抽风,nvm 也支持对应的 环境变量
export NVM_NODEJS_ORG_MIRROR=https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/node
Rustup
Rustup 要相对更加简单的一点,Rustup 默认会读取两个环境变量,将其修改为镜像站点即可:
export RUSTUP_DIST_SERVER=https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/rust-static
export RUSTUP_UPDATE_ROOT=https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/rust-static/rustup
然后再用官方的脚本。
curl https://sh.rustup.rs -sSf | sh
source $HOME/.cargo/env
对于 Windoiws 环境则需要在“设置”-“高级系统设置”-“环境变量”中添加对应的变量到用户/系统变量中。
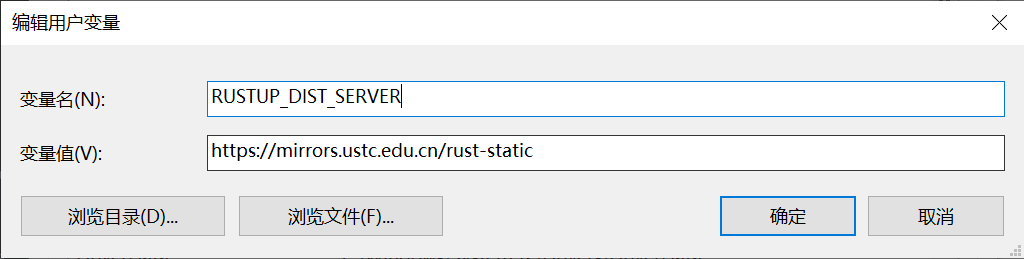 Windows environmentail
Windows environmentail
当然这几个主要的变量可以放在 .zshrc 中,以后更新还会用到的。
Crate.io
~/.cargo/config 清华大学赛高。
[source.crates-io]
replace-with = 'tuna'
[source.tuna]
registry = "https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/git/crates.io-index.git"
对于 Windows 环境,则需要 C:\Users\{username}\.cargo 目录下的 config 文件,添加对应的源地址。
Go mod
Go mod 支持 proxy 设置:
go env -w GO111MODULE=on
# 1. 七牛 CDN
go env -w GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn,direct
# 2. 阿里云
go env -w GOPROXY=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/goproxy/,direct
# 3. 官方
go env -w GOPROXY=https://goproxy.io,direct
pypi
同样清华大学的源,pypi 镜像每 5 分钟同步一次。
pip install pip -U
pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
如果到 pip 默认源的网络连接较差,临时使用本镜像站来升级 pip:
pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple pip -U
对于本机
目前主要是使用 WSL2 中的 Ubuntu 作为开发环境的,WSL2 目前比较大的问题就是每次其 IP 地址都会变动,宿主机的地址,也就是它的网关也会一直变。
好在 DNS 地址默认就是宿主机 Windows 的地址,可以通过一个简单的命令查到它并将其保存到当前环境变量中:
# 主机 IP 保存在 /etc/resolv.conf 中
export host_ip=$(cat /etc/resolv.conf |grep "nameserver" |cut -f 2 -d " ")
alias winip='cat /etc/resolv.conf |grep "nameserver" |cut -f 2 -d " "'
顺便把内容单独提取到一个小脚本中:
HOST_IP=$(cat /etc/resolv.conf | grep nameserver | awk '{ print $2 }')
WSL_IP=$(hostname -I | awk '{print $1}')
PROXY_PORT=10809
PROXY_HTTP="http://${HOST_IP}:${PROXY_PORT}"
set_proxy() {
export http_proxy="${PROXY_HTTP}"
export HTTP_PROXY="${PROXY_HTTP}"
export https_proxy="${PROXY_HTTP}"
export HTTPS_proxy="${PROXY_HTTP}"
export ALL_PROXY="${PROXY_SOCKS5}"
export all_proxy=${PROXY_SOCKS5}
git config --global http.proxy ${PROXY_HTTP}
git config --global https.proxy ${PROXY_HTTP}
# git ssh proxy
sed -i "s/# ProxyCommand/ProxyCommand/" ~/.ssh/config
sed -i -E "s/ProxyCommand nc -X connect -x [0-9]+\.[0-9]+\.[0-9]+\.[0-9]+:[0-9]+ %h %p/ProxyCommand nc -X connect -x ${HOST_IP}:${PROXY_PORT} %h %p/" ~/.ssh/config
}
unset_proxy() {
unset http_proxy
unset HTTP_PROXY
unset https_proxy
unset HTTPS_PROXY
unset ALL_PROXY
unset all_proxy
git config --global --unset http.proxy ${PROXY_HTTP}
git config --global --unset https.proxy ${PROXY_HTTP}
sed -i -E "s/ProxyCommand nc -X connect -x [0-9]+\.[0-9]+\.[0-9]+\.[0-9]+:[0-9]+ %h %p/# ProxyCommand nc -X connect -x 0.0.0.0:0 %h %p/" ~/.ssh/config
}
test_proxy() {
echo "Host ip:" ${HOST_IP}
echo "WSL ip:" ${WSL_IP}
echo "Current proxy:" ${https_proxy}
}
并放在 .zshrc 中,使其可以自动被设置:
# This is proxy for git.
. ~/.config/proxy.sh
set_proxy

